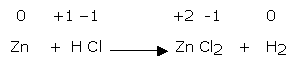Balancing of REDOX REACTION
Balancing of REDOX REACTION
Two types of Balancing of REDOX REACTION:
There are two very important methods for balancing oxidation-reduction reactions. These are:
1).Oxidation number method
2).Ion-electron method
Oxidation Number Method
During a redox reaction, the total increase in oxidation number must be equal to total decrease in oxidation number. Here, (the law of conservation of mass should not be violated). The following steps should be followed:
Steps for balancing redox equations by oxidation number method
1. Write the skeleton redox reaction.
2. Indicate the oxidation number of atoms in each compound above the symbol of the element.
3. Identify the element or elements, which undergo a change in oxidation number, one whose oxidation number increases (reducing agent) and the other whose oxidation number decreases (oxidizing agent).
4. Calculate the increase or decrease in oxidation numbers per atom. Multiply this number of increase/decrease of oxidation number, with the number of atoms, which are undergoing change.
5. Equate the increase in oxidation number with decrease in oxidation number on the reactant side by multiplying the formulae of the oxidizing and reducing agents.
6. Balance the equation with respect to all other atoms except hydrogen and oxygen.
7. Finally, balance hydrogen and oxygen.
8. For reactions taking place in acidic solutions, add H+ ions to the side deficient in hydrogen atoms.
9. For reactions taking place in basic solutions, add H2O molecules to the side deficient in hydrogen atoms and simultaneously add equal number to OH- ions on the other side of the equation.
Let us discuss the above method stepwise with the help of reaction between zinc and hydrochloric acid.
Step 1
The skeleton equation is:
Zn + HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
Step 2
Oxidation number of various atoms involved in the reaction
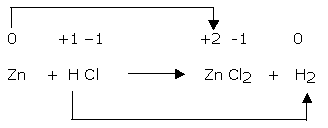
Step 3
The oxidation number of zinc has increased from 0 to +2 while that of hydrogen has decreased from +1 to 0. However, the oxidation number of chlorine remains same on both sides of the equation. Therefore, zinc is reducing agent while HCl is oxidizing agent in reaction and the changes are shown as:
Step 4
The increase and decrease in oxidation number per atom can be indicated as: O.N. increases by 2 per atom
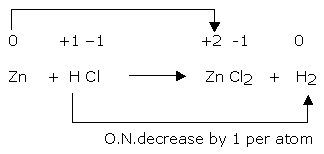
Step 5
The increase in oxidation number of 2 per atom can be balanced with decrease in oxidation number of 1 per atom if Zn atoms are multiplied by 1 and HCl by 2. The equation will be:
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
Problem
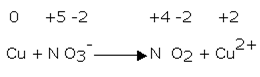
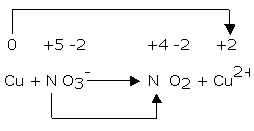
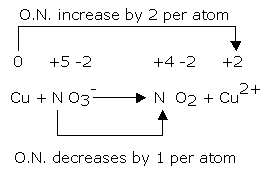
1. Copper reacts with nitric acid. A brown gas is formed and the solution turns blue. The equation may be written as:
Cu + NO3- → NO2 + Cu2+
Balance the equation by oxidation number method.
Solution
Step 1
Skeleton equation
Cu + NO3- → NO2 + Cu2+
Step 2
Writing oxidation numbers of each atom
Step 3:
The oxidation number of copper has increased from 0 to +2 while that of nitrogen has decreased from +5 to +4.
Step 4
Show, the increase/decrease of oxidation number
Step 5
Balance the increase/decrease in oxidation number by multiplying NO3- by 2 and Cu by 0.
Cu + 2NO3- → NO2 + Cu2+
Step 6
Balance other atoms except H and O as
Cu + 2NO3- → 2NO2 + Cu
Step 7
Reaction takes place in acidic medium, so add H+ ions to the side deficient in H+ and balance H and O atoms:
Cu + 2NO3- + 4H+ → 2NO2 + Cu + 2H2O
Balancing redox reactions by ion-electron method
The balancing of a chemical equation by ion-electron method (using half reactions) is done according to the following steps:
1. Find the elements whose oxidation numbers are changed. Choose the substance, which acts as an oxidizing agent and one that acts as a reducing agent.
2. Separate the complete equation into two half reactions, one for the change undergone by the oxidizing agent and the other for the change undergone by the reducing agent.
3. Balance half equations by the following steps:
a) Balance all atoms other than H and O.
b) Calculate the oxidation number on both sides of the equation and add electrons to whichever side is necessary, to make up the difference.
c) Balance the half equation so that both sides get the same charge.
d) Add water molecules to complete the balancing of the equation.
4. Add two balanced half equations. Multiply one or both half equations by suitable numbers so that on adding the two equations, the electrons are balanced.
Redox reactions take place in all the three media acidic or basic or neutral. If H+ ions appear on either side of the equation, the reaction takes place in acidic medium. If OH- ions appear on either side of the equation, the solution is basic. If neither H+ nor OH- ions are present, the reaction occurs in neutral solution. For balancing redox reactions involving acidic and basic media, the method has to be modified slightly.
 SureDen
SureDen