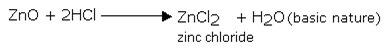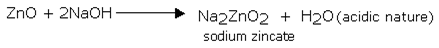Types of oxides
Types of Oxides:
Oxides are binary compounds of oxygen with another element, e.g., CO2, SO2, CaO, CO, ZnO, BaO2, H2O, etc. These are termed as oxides because here, oxygen is in combination with only one element. Oxides are classified as acidic, basic, amphoteric, or neutral:
a) Acidic oxides:
Acidic oxides are the oxides of non-metals. When combined with water, they produce acids. Acidic oxides are, therefore, known as acid anhydrides, e.g., sulphur dioxide is sulphurous anhydride; sulphur trioxide is sulphuric anhydride.
When these oxides combine with bases, they produce salts, e.g.,
SO2 + 2NaOH → Na2SO3 + H2O
b) Basic oxides:
Basic oxides are the oxides of metals. If soluble in water they react with water to produce hydroxides (alkalies). These metallic oxides are therefore, known as basic anhydrides.
CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
MgO + H2O → Mg(OH)2
Na2O + H2O → 2NaOH
They react with acids to produce salts. e.g.,
MgO + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2O
Na2O + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O
c) Amphoteric oxides:
Amphoteric oxides are metallic oxides, which show both basic as well as acidic properties. When they react with an acid, they produce salt and water, showing basic properties. While reacting with alkalies they form salt and water showing acidic properties, e.g.,
Al2O3 + 3H2SO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2O (basic nature)
Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O (acidic nature)
d) Neutral oxides:
These are the oxides, which show neither basic nor acidic properties, that is, they do not form salts when reacted with acids or bases, e.g., carbon monoxide (CO); nitrous oxide (N2O); nitric oxide (NO), etc., are neutral oxides.
e) Per-oxides and dioxides:
Peroxide: It is a metallic oxide which gives hydrogen peroxide by the action of dilute acids. They contain more oxygen than the corresponding basic oxide, e.g., sodium, calcium and barium peroxides.
BaO2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + H2O2
Na2O2 + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O2
Dioxide: like PbO2 and MnO2 also contain higher percentage of oxygen like peroxides and have similar molecular formulae. These oxides, however, do not give hydrogen peroxide by action with dilute acids. Dioxides on reaction with concentrated HCl yield Cl2 and on reacting with concentrated H2SO4 yield O0.
Pb O2 + 4 HCl → PbCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O
2PbO2 + 2H2SO4 → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O + O2
e) Compound oxides:
Compound oxides are metallic oxides and they behave as if they are made up of two oxides, lower and higher oxides of the same metal, e.g.,
Red lead: Pb3O4 = PbO2 + 2PbO
Ferro-ferric oxide: Fe3O4 = Fe2O3 + FeO
On treatment with an acid, compound oxides give a mixture of salts.
Fe3O4 + 8HCl → 2FeCl3 + FeCl2 + 4H0O
Ferro – ferric oxide → ferric chloride + ferrous chloride
 SureDen
SureDen