Solvent property of water
Solvent property of water:
The polarity of water: Water has a simple molecular structure. It is composed of one oxygen atom and
two hydrogen atoms. Each hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to the oxygen via a shared pair of electrons. Oxygen also has two unshared pairs of electrons. Thus there are 4 pairs of electrons surrounding the oxygen atom, two pairs involved in covalent bonds with hydrogen, and two unshared pairs on the opposite side of the oxygen atom. Oxygen is an "electronegative" or electron "loving" atom compared with hydrogen.
Polarity: refers to a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole. . The ability of ions and other molecules to dissolve in water is due to polarity.
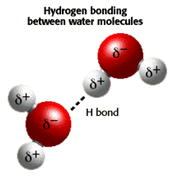
- Water is a "polar" molecule because there is an uneven distribution of electron density
- Water has a partial negative charge near the oxygen atom due to the unshared pairs of electrons, and partial positive charges near the hydrogen atoms.
- An electrostatic attraction between the positive and negative charge results in the formation of a hydrogen bond.
Acids and Bases, Ionization of Water:
• Acid release H+
• Bases accept H+
Some important points:
• At pH 7.0, a solution is neutral
• At lower pH (1-6), a solution is acidic
• At higher pH (8-14), a solution is basic
 SureDen
SureDen