Sources of hydrocarbons
Origin of coal and petroleum
Coal and petroleum have organic origin, being decomposed plant and animal matter buried deep inside the earth. Coal is mined like any other mineral.
The chief coal producing countries in the world are China, U.S.A., U.S.S.R., U.K., Germany, Poland, Australia and India. In India, coal is mainly mined in Bihar, West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh and to some extent in Andhra Pradesh.
Petroleum occurs deep inside the Earth at depth ranging from a few hundred to few thousand meters. The name petroleum has been given to the crude oil because it occurs under the Earth's crust entrapped in rocks (petra = rocks oleum = oil). Crude oil (petroleum) is pumped out of Earth by drilling oil wells. Petroleum is obtained by drilling a hole through the crust till it reaches the oil reserve. The oil gushes out of its own due to high pressure of the gas over its surface. However, when the pressure falls, it is pumped out with the help of pumps. Large quantity of natural gas is generally associated with petroleum. Petroleum is often referred to as liquid gold, due to its importance in transportation, commerce and industry. Prosperity of any country depends upon its petroleum reserves.
The chief petroleum producing countries are, U.S.A., U.S.S.R., Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Iraq, Iran, Libya, Nigeria, Algeria, Venezuela China and Mexico.
Composition of coal and petroleum
Coal is mainly composed of carbon. Coal, is classified into different varieties depending upon its carbon content. Common varieties of coal are,
Variety of coal: Peat Lignite Bituminous AnthraciteCarbon content:10-15% 40% 60-70% 80-90%
Coal also contains arenes or aromatic hydrocarbons like benzene, toluene, xylene, naphthalene and anthracene. It also has some organic compounds of sulphur and nitrogen.
Crude oil (or petroleum) is a dark brown viscous liquid sometimes having a greenish tinge. Crude oil is a mixture of about 150 different organic compounds. Crude oil is largely made up of aliphatic hydrocarbons, with much lesser amounts of aromatic compounds and organic compounds of sulphur and nitrogen.
Formation of coal and petroleum in nature
It is believed that coal in nature was formed from the remains of the trees buried inside the earth some 500 million years ago. Due to the bacterial and chemical action on the wood, it got converted into peat. Then, as a result of high temperature and high pressure inside the earth peat got transformed into coal.
It is believed that the petroleum was formed from the partial decomposition of the sea animals and prehistoric forests under high temperature and pressure conditions inside the earth.
hydrocarbon from petroleum
Crude oil or petroleum pumped out of an oil well, is a viscous and complex mixture of several hydrocarbons and small amounts of other compounds. It is not useful in this state. The 'refining of (crude) petroleum' involves the process of fractional distillation, whereby petroleum is separated into many useful fractions.
Refining of crude oil
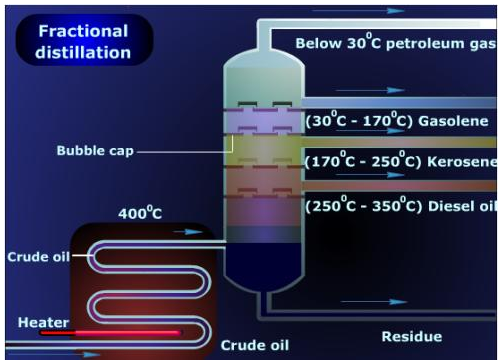
The refining of petroleum is done in big refineries. Washing it with acidic or basic solution first neutralizes crude oil. A furnace is used to heat up the crude oil to 650 - 675 K and then the pressure reduced. The resulting crude oil vapors are fed into a fractionating column through an inlet near the bottom of the furnace.
Fractional distillation of crude oil
The fractionating tower is a tall cylindrical steel structure divided into compartments by horizontal trays fitted into it. Each tray has a number of holes and a short tube with a bubble cap. Due to a regular temperature gradient along the height of the column, the fractions with lower boiling points rise up and get liquefied at different heights in the trays, depending on the boiling. These caps allow the lighter vapors to escape up the column while the progressively less volatile and heavier fraction condense and flow into the respective trays (through tray holes and overflow) in the lower section of the tower. They can then be tapped out. The major products obtained from the fractional distillation of crude oil are listed below. Gasoline obtained by this procedure is called straight run gasoline.
|
Product |
Chain length |
Boiling range |
Uses |
% |
|||
|
Gas |
C1 to C5 |
Below room temperature |
As fuel: in manufacture of gasoline rubber, carbon black. Ammonia and methane black. |
2 |
|||
|
Petroleum ether |
C5 to C7 |
303 – 363 K |
As a solvent and in dry cleaning. |
2 |
|||
|
Petrol |
C7 to C12 |
343 – 473 K |
Motor fuel: dry cleaning solvent. |
32 |
|||
|
Kerosene |
C1 to C16 |
440 – 540 K |
As a fuel and illuminant. |
18 |
|||
|
Gas oil Fuel oil diesel |
C15 to C18 |
523 – 673 K |
Furnace fuel: diesel engine fuel: in cracking |
20 |
|||
|
Residue products:- Lubrication oil, greases, petroleum jelly
|
C16 and up |
623 and up |
As lubricant, in medicines and cosmetics (petrol jelly) |
||||
|
Paraffin wax
|
C20 and up |
Melts at 325 – 330 K |
Makinu candles and water proofinq. |
||||
|
Petroleum coke
|
C30 and up |
Residue |
As a fuel for makinu electrodes. |
||||
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG)
Petroleum gas a by-product from two sources: natural gas processing and crude oil refining is a mixture of butane, propane and ethane. The main constituent of liquefied petroleum gas is, however, propane, propylene, butane, butylene in various mixtures. These hydrocarbons burn readily, producing a large amount of heat. This makes petroleum gas a very good fuel.
Large quantities of propane and butane are now available from gas and petroleum industries. These are often employed as fuel for tractors, trucks, and buses and mainly as a domestic fuel. They are gases under ordinary pressure. Because of the low boiling point (-44 to 0°C) and high vapor pressure of these gases, their handling as liquids in pressure cylinders is necessary. Thus, they can be easily liquefied under pressure. The petroleum gas, which has been liquefied under pressure is called Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG).
Petroleum gas is supplied in liquid form so that a cylinder of even small volume may contain an appreciable amount of the gas. A domestic gas cylinder whose main constituent is butane, contains about 14 kg of LPG. A strong smelling substance (Ethyl mercaptan C2H5SH) is added to LPG gas cylinders to help in the detection of gas leakage. The gas used for domestic cooking is called Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) because it is present in liquid form in the cylinders and is commonly used for domestic heating purposes.
Owing to demand from industry for butane derivatives, LPG sold as fuel for automobiles is made up largely of propane. This is because,
• LPG compares favorably in cost per mile.
• It has a high octane rating making it useful in engines too.
• LPG leaves little or no engine deposit in the cylinders when it burns, a factor of importance in internal combustion engines.
• As it enters the engine as a vapor, it cannot wash down the cylinder walls, remove lubricant, and increase cylinder-wall piston and piston-ring wear.
All these factors reduce engine wear, increase engine life, and maintenance costs low.
Compressed natural gas (CNG) and Liquid natural gas (LNG)
A liquefied form of natural gas usually consists primarily of methane. Its properties are those of liquid methane, slightly modified by minor constituents. One property, which differentiates liquefied natural gas (LNG) from liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), which is principally propane or butane or both, has a much lower critical temperature, about (-73°C). Unlike LPG, natural gas cannot be liquefied at normal ambient temperature by increasing pressure; natural gas must be cooled to cryogenic temperatures to be liquefied and then stored in well-insulated containers. CNG or LNG is stored in high pressure cylinders or special tanks.
The natural gas is compressed or liquefied for ease of storing and transporting. LNG takes up about (1/600) the space that natural gas does in its gaseous form. LNG technology has made it possible to utilize natural gas from remote areas where it previously had no common use and was burned. CNG or LNG are very clean fuels, which cause very little pollution and have very high calorific value.
 SureDen
SureDen