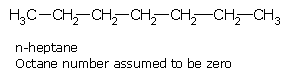Octane Number
Quality of petrol (gasoline) - octane number
The controlled combustion of fuel in the presence of air, gives an internal combustion engine its power. A low quality fuel does not burn smoothly and causes an occasional explosive sound, which is known as knocking. This greatly reduces the power of the engine.
The quality of a fuel is indicated in terms of its octane number. Different hydrocarbons have different knocking tendencies. A fuel that produces minimum knocking is considered as a good fuel.
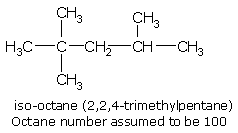
An arbitrary scale of octane number has been set up with n-heptane and 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (iso-octane) as the reference compounds. All fuels are graded in between these two limiting values by comparing with a suitable mixture of the above two compounds. 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (generally called iso-octane) has excellent anti-knocking properties and has been arbitrarily assigned an octane number of 100, whereas n-heptane, which is very prone to knocking is assigned an octane number of zero (0). Therefore, the antiknock property of a fuel increases with the increase in its octane number.
Thus, the octane number of any fuel is defined 'as the percentage of iso-octane in a mixture of iso-octane and n-heptane that has the same knocking as the fuel under examination'.
A fuel having an octane number of 80 behaves in a manner similar to a mixture having 80% of iso-butane, and 20% of n-heptane. Straight run gasolines may have octane values ranging from 20 to 73. Aviation fuel is rated as 100 octane.
The octane number of a hydrocarbon depends upon its structure.
• Branched-chain alkanes, alkenes and aromatic hydrocarbons have high octane numbers. Such compounds are added to straight-run gasoline to raise its octane number. These high octane compounds, viz., branched-chain alkanes, alkenes, and aromatic hydrocarbons are prepared by catalytic cracking and catalytic reforming.
• Straight chain alkanes have low octane numbers, the value of which decreases with the increase in the length of the chain.
• Cyclic alkanes have higher octane numbers than the corresponding straight chain alkanes.
• The unsaturated hydrocarbons have higher octane numbers than the corresponding straight chain hydrocarbons.
• Aromatic hydrocarbons have very high octane numbers.
Octane ratings of some compounds are:
n-Heptane 0
n-Pentane 62
tert-butyl alcohol 98
neo-octane Benzene 100
Ethanol 112
Methanol 116
Toluene 118
 SureDen
SureDen