Periodic Properties
Periodic Properties:- The properties which are directly / indirectly related to their electronic configuration and which show a regular gradation when we move from left to right (periods) or from top to bottom (groups) in group.
Example- Imisation Energy, Atomic Radius etc.
(1) Atomic size / Atomic Radius:- It is defined as the distance from the centre of nucleus & outermost shell: It is expressed in terms of A0, pm and nm.
Types of Atomic Radius:-
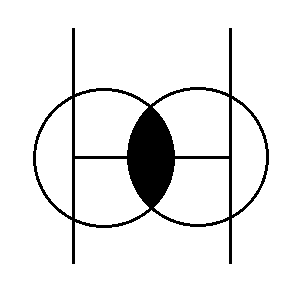
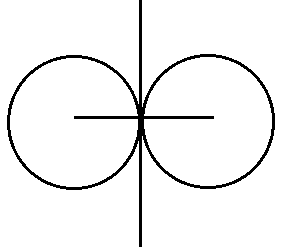
(i) Covalent Radius- half of the inter nuclear –distance between two bonded atoms in same molecules.
(ii) Metallic Radius- half of the internuclear distance between two atoms joined by metallic bond.
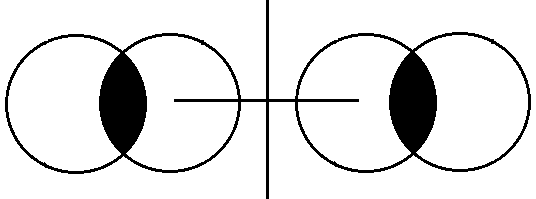
(iii) Vanderwall Radius- internuclear distance between the two atoms of two different molecules / or tow niqbouring atoms.
Increasing order of atomic radius:-
Covalent- Radius < Radius < Vanderwall Radius
Trend of Atomic size in a group and periods.
|
Groups (top to bottom) Trend:- From top to bottom in a group, size increases. Reason:- (a) Number of shells increases and distance between nuclear and outermost shell increases. (b) Screening, increasing / Shielding effect
|
Periods (left to right) Trend:- (a)From left to right in a period, atomic size decreases. Reason:- Effective Nuclear charge increases (b) Number of shells remains same.
|
Exceptional Cases in groups
B The size of gallium (Ga) is smaller than that of
Al Aluminium (Al) because in gallium
Ga effective nuclear charge increases due to
In poor shielding effect of nucleus by Third electrons
Te
Effective Nuclear Charge (ENC):- The nuclear charge felt by the electron
Effective Nuclear Charge = Actual Nuclear charge ― Screening effect
At the end of the period, the atomic size of noble gases increases because of fully filled configuration, inter- electronic repulsion increases and size expands and also noble gases show vanderwall radius which is larger
 SureDen
SureDen