Chemical Properties and Periodicity
Chemical Properties and Periodicity:-
(1) Valency:- (a) It is the combining capacity of an element.
(b) It is either equal to the number of valence electron or (8 – number of Valence electrons).
Trend of valency Along the groups / periods.
|
Periods |
Groups |
|
Trend:- Trom left to right valency increases from 1 to 4 than decreases to O. |
In top to bottom valency remains same because of similar number of valence electrons. example- Alkaline Metals have 2 valency |
Write down the compound formed between following pairs?
(a) Mg+2 and N3- Mg3N2
(b) Element 7I and F CuF3
(c) Si and S Si S2
(d) Si+4 and O2- Si O2 or Si2 O4
(e) Ca+2 and O2- Ca O
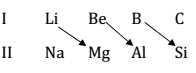
(2) Diagonal Relationship (DR):- It is the similarity in propect of elements of second period and third period placed drag only in periodic table.
Cause of Diagonal Relationship:- Similar ionic size
(b) Similar polarizing power Ionization energy charge / size ratio.
Ionization energy tendency to attract the electron cloud of anion by a cation in ionic bind.
Important points:-
(a) In a periodic table more than 75% are metals these are normally placed on left hand side of the periodic table.
(b) Transition from metallic to non-metallic behavior is not abrupt Via semi-metals or metalloids example:- Si, Te.
(c) Group 17) Ionisation energy halogens has metals, non-metals, gases, liquid, solids.
(d) In case of metals reactivity increases from top to bottom and Ionisation Energy decreases and Metals Reducing character increases from top to bottom
(e) In case of non-metals (halogens) reactivity decreases from top to bottom and electron gain enthalpy less negative.
 SureDen
SureDen