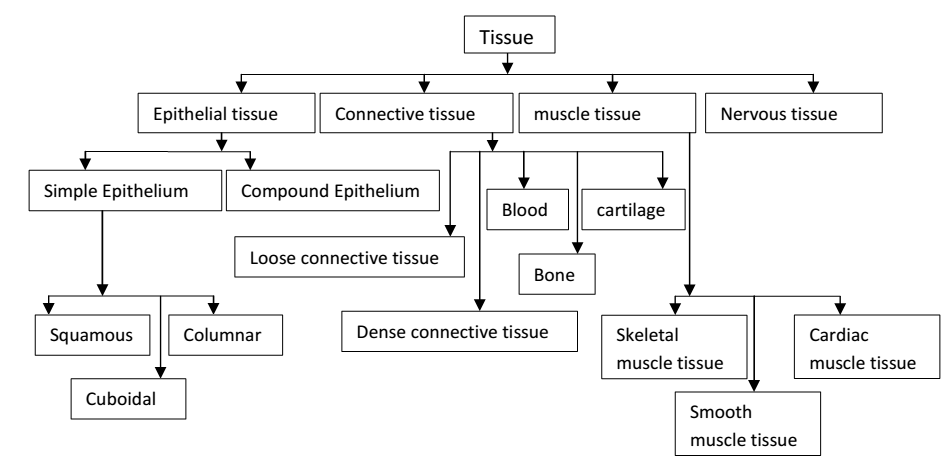
Type of Tissue
- Epithelial tissue:-
Definition à the tissue composed of one or more layer of cells which mainly covers body and lining cavities, hollow organs and tubes is called epithelial tissue.
Function :-
- protection of underlying structure from dehydration, chemical and mechanical damage.
- Secretion
- Absorption
Structure :-
- Cells are very closely packed.
- The intracellular substance is minimal.
- The cells are usually lie on basement membrane.
- There are two types of epithelial tissue.
a)Simple epithelium b) compound epithelium
a) simple epithelium :- consist of single layer of identical cells. It is divided into 3 types according to shape of cell.
-Simple squamous epithelium
-Simple cuboidal epithelium
-Simple columnar epithelium
Simple squamous epithelium :-
It is composed of single layer of flat cells.
It is forms the lining of structure like heart, lymph vessels, capillaries, alvedi of lungs etc.
Simple cubaidal epithelium :-
It is composed of single layer of cube shape cells. e.g. tubules of kidney.
Simple columnar epithelium :-
it consist of single layer of reticular cells on basement membrane. e.g. lining of stomach. Surface of columnar lining trachea is covered with cilia and contain goblet cell that secrete mucus also known as glandular epithelium.
On the bases of secretion, glands are divided in 2 categories :
- Exocrine :- secretion which are released from ducts or tubes is from exocrine gland. e.g. solving gland, pancreas.
- Endocrine :- the glands which don’t have ducts. Their products ore called hormones.
(b) Compound Epithelium :-
It consist of several layer of cells of various shapes.
Continuous division in the lows layer push cell above nearer and nearer to surface, where they shed.
Basement membrane are usually absent.
There are two types of compound epithelium.
(1) compound squamous epithelium (2) transitional epithelium.
- Compound squanous epithelium :-
It is composed of no. of layers of cell. It is of two types :-
Keratinized : 1) Found on dry surface, subjected to wear and tear. e.g. skin, hair or nail.
2) Surface layer consist of that epithelial cells that have last their nucleus and contain keratin.
3) This from a tough, waterproof, protective layer that present drying of live cells underneath.
Non-keratinized : This protect moist surface subjected to wear and tear and present them from drying.
e.g. conjunctive of eye, lining of mouth, oerophages, pharynx.
(2) Transitional epithelium :-
Composed of many layers of pear shaped cells.
It is found in lining urinary bladder and allow for stretching as bladder fills.
- Connective tissue :-
Definition – the tissue which links and supports other organs and tissues is called connective tissue.
Structure :- cells are more widely separated from each other.
An intracellular substance is present in large amount.
There are usually fibers present in matrix.
Functions :-
- Binding and structural support.
- Insulation.
- Transport.
- Protection.
Types of connective tissue
- Loose / areolar connective tissue.
- Dense connective tissue.
- Specialized connective tissue.
- Loose/ areolar connective tissue
This is the most generalized type of connective tissue.
Matrix is semisolid with many fibroblasts, some fat cells, most cells and macrophages widely separated by elastic and collogen fiber.
It is found in every part of body almost, providing elasticity and tensile strength.
It connects and support other tissues.
Adipose Tissue :- This tissue lies mainly beneath spin. It consist of fat cells. the exercise nutrients which are not used, store in this tissue in form of fat.
(ii) Dense connective tissue :-
This tissue contain more fibers and fiber blasts and few cells as composed to loose connective tissue. It is further of two types.
Dense regular :- this tissue is made up of mainly closely packed bundles of collagen fiber with very little matrix.
Fibrocytes ( old and inactive fibroblasts) are few in number and are found b/w bundles of fibers.
e.g. in large blood vessels, trachea , lungs etc.
(iii) Specialized connective tissue.
It include cartilage, Bones and blood.
Cartilage :- It is firmer than other connective tissue.
The cells are called chondrocyte and are less in number.
They are found in matrix reinforce by collagen fiber.
Blood :- It is fluid connective tissue which consist of RBC, WBC and platelets.
Bone :- Bone cells osteocyte are surrounded by matrix of collagen fiber strengthen by inorganic salt specially calcium and phosphate.
This provide bones with their characteristic strength and rigidity.
(c) Muscular tissue
Muscular tissue is able to contract and relax.
It provide movement within the body and of body itselt.
There are 3 types of specialized contractile all called :-
- Skeletal muscle tissue
- Smooth muscle tissue
- Cardiac muscle tissue
- Skeletal muscle tisse:-
It is named so because it forms those muscles that move bones.
It is also called striated because strips can be seen on micro- scopic observation.
It is called voluntary as it is under conscious control.
Fibers are cylindrical, contain several nucleus and may be upto 35 cm long.
Skeletal muscle contraction is stimulated by motor nerve impulses originate in brain or spinal cord.
- Smooth muscle tissue
It is called non-striated, visceral or involuntary.
It doesn’t have striper and it is not under conscious control.
Smooth muscle has intrinsic ability to contract and relax.
Autonomic nerve impulses, some hormones and local metabolite stimulate contraction.
It is found in the wall of hollow organs such as blood vessels.
The cells of smooth muscle tissue are spindle shape with one nucleus.
- Cardiac muscle tissue
This type of tissue found only in wall of heart.
It is involuntary, but cross strips characteristic of skeletal muscle can be seen on micro skopic examination.
Each fiber has nucleus and one as more branches.
The end of the cell and their branches, are in very close contact.
These joint or intercalated disc can be seen as line that are thick and dark than ordinary cross strips.
A wear of contraction spread from cell to cell across the intercalated disc, which mean that cell don’t need to stimulated individually.
- Nervous tissue
This tissue controls over body’s responsiveness to charging conditions.
Two type of cells are found in nervous system :-
- Excitable cells :- neuron are called excitable cells, is unit of nervous system.
They initiate, receive, conduct and transmit information.
Arrival of the disturbance at neuron’s ending or output zone, triggers went that may cause stimulation or inhibition of adjacent neurons and others.
- Non- excitable cells :- These are called glial cells.
These support the neurons.
More than one half of the nervous tissue is made up of neuroglia.
 SureDen
SureDen