Placentation
Placentation
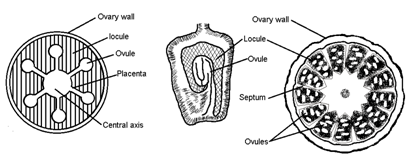
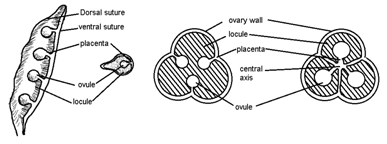
Types of placentation
- Marginal : In the monocarpellary (Pea) or each carpel of multicarpellary apocarpous gynoecium, there is single placenta which develops along the junction of two fused margins.
- Parietal : When the gynoecium is formed by the fusion of two or more carpels by their adjacent margins, the ovary is unilocular and has two or more longitudinal plecenta or inner wall of the ovary e.g., Cucurbita, Brassica.
- Axile : In a multicarpellary syncarpous gynoecium the fusing margins grow inwards to meet in the center of the ovary to form an axis thus making the ovary, e.g., China rose, Tomato, Lily.
- Free Central : The ovary is unilocular and the ovules are borne on the axis in the center of the ovary e.g., Dianthus.
- Basal : The ovary is unilocular and a single ovule is borne at the base of the ovary e.g., Sunflower, Rice, Wheat.
- Superficial : The gynoecium is multicarperllary syncarpous and large number of ovules are borne on the walls of loculi without specific order e.g., Nymphaea (Water lily).
-
Related Keywords
 SureDen
SureDen