Modification of Roots
Modification of tap root:-
Fleshy roots:-
- Fusiform: In these roots the middle portion becomes thicker and tapers on both the ends, e.g. Raphanus sativus (radish).
- Conical: These roots have broad base tapering towards the apex, e.g. Daucas carota (carrot).
-
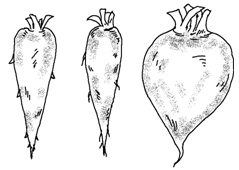
- Tuberous: This root have irregular shape e.g. Mirabilis jalapa
-
-
Other modification of adventitous Roots:-
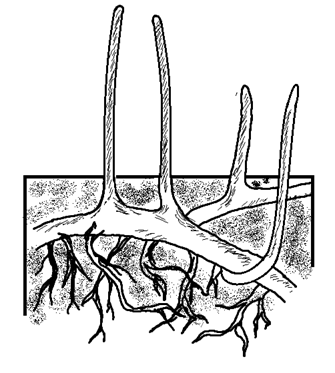
- Prop roots:- Roots arise from horizontal arial branches. Initially, they are hygroscopic. They grow vertically downward, penetrate the soil, become thick and assume the shape of pollars. e.g. Ficus bengalensis.
- Stilt roots:- In some plants roots are formed from the nodes of lowermost portion of the stem and provide mechanical support to the plant by fixing it in soil firmly, pandanus tinctorius (screw pine).
- Climbing roots:- Some climbers climb up their support with the help of climbing roots which arise from the nodes and twine round the support, e.g. Pothos, Piper.
- Contractile or Pull roots: some roots of plants with underground stems contract or swell so that the arial shoots are in a proper depth in the soil. e.g. Crocus, Canna, Allium, Freesia.
- Foliar roots:- When leaf is modified into roots. e.g., Salvinia, three leaves arise from each node. Two of them are normal leaves but one gets modified into roots for balancing.
- Root thorns:- In Pothos, Acanthorrhiza and Iriartea, some adventitious roots form the base of stem become hard and thorn like.
- Haustorial roots:- The roots of parasitic plants, which penetrate into the host tissue to absorb nourishment. e.g., Cuscuta, Viscum
- Epiphytic roots:- Some epiphytes, e.g. orchids have aerial roots. These roots absorb moisture from atmosphere with the help of velamen tissue.
- Floating roots:- These roots store air, become inflated and spongy, project above the level of water, make the plant light and function as floats. e.g., Jussiaea.
- Assimilatory roots:- In some plants the roots develop chlorophyll, e.g. Tinospora, Trapa, etc.
- Root thorns:- Roots of some plants arise from the stem and change into thorns, performing the protective function, e.g. Pothos (money plant).
Related Keywords
 SureDen
SureDen