Forms and Types of Stem
Forms of Stem:
- Strong Stem:
The following terms are important in relation to strong stems.
- Excurrent:- The main axis shows continues growth and the lateral branches develop regularly giving a conical appearance to the trees; Pinus.
- Deliquescent:- The growth of lateral branch is more vigorous than that of main axis. The tree has a rounded or spreading appearance; e.g. Mangifera, Ficus.
- Caudex:- It is unbranched, stout, cylindrical stem, marked with scars of fallen leaves; e.g. Cocos, Date-palm.
- Clum:- Erect stems with distinct nodes and internodes. Stem shows jointed appearance. e.g. Bambusa arundinacea.
Branching of stem
Stem branching is of three types:
- Dichotomous: Pandanus, Asclepias.
- Racemose (Monopodial): Pinus, Eucalyptus.
- Cymose: a) Sympodial or uniparous cyme. e.g., Saraca (Helicoid), Grape (Scorpoid).
b) Dichasial cyme: e.g. Viscum, Datura.
c) Polychasial cyme : e.g., Euphorbia, Croton.
Types of stem
Weak Stem:
Theses stems cannot maintain an upright position. Weak stems can be divided into following categories:
Trailing:
It is a weak stem that spreads over the surface of the ground without rooting at the nodes. These fall into three categories:
- Prostrate (procumbent): A stem that lies flat on the ground.
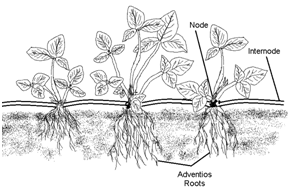
Creeping:
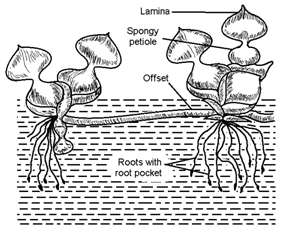
The plant grows horizontally on the ground and gives off roots at each node; e.g. grasses, strawberry, Oxalis. Runners, stolons, offset and suchers.
- Climbing:
This week stem climbs a support by means of some special structure or organ for attachment. These are divided into following types.
- Twiners : It is week, long and slender stem that climbs by twining is body around the support.
- Tendril Climbers : It is a week stem climbing by its slender, leafless, spirally coiled structures, known as tendrils.
- Leaf tendril : The whole leaf is modified into a tendril.
- Leaflet tendril : Some upper leaflets of a leaf are modified into a tendril.
- Petiole tendril : Petiole is modified into a tendril e.g., Clematis.
- Leaf apex tendril : Apex of a leaf is modified into a tendril e.g. , Gloriosa.
- Stipule tendril : Stipule is modified into a tendril e.g., Smilax.
- Apical bub tendril : Apical bub is modified into a tendril e.g. , Vitis.
- Axillary bub tendril : Axillary bub is modified into a tendril e.g., Passiflora (Passion flower).
- Extra axillary bub terndril : e.g. cucurbits.
- Inflorescence axis tendril : Inflorescence axis is modified into a tendril e.g., Antionan.
- Root climbers : Such climbers give out adventitious roots at each node which stick to the support; e.g. Pothos scandens (money plant).
- Hook climbers (Scramblers) : In Bougainvillea.
-
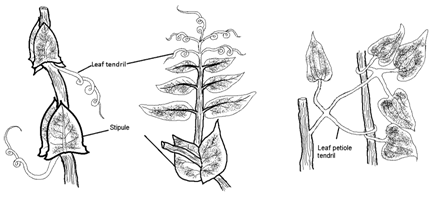
-

- Lathyrus - Whole leaf modified into tendril
- Pisum sativum – Upper leaflet modified into tendril,
- Clematis – Petiole modified into tendril,
- Gloriosa – Leaf apex modified into tendril,
- Smilax – Stipule modified into tendril.
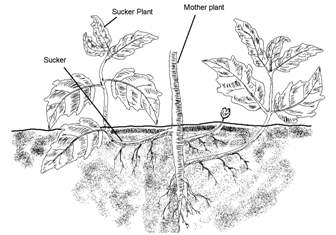
Sucker :- Arising from the basal underground portion of the main. Initially it grows horizontally below the surface of the earth but soon grows obliquely upward forming a leafy shoot e.g. Chrysanthemum.
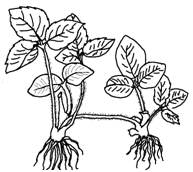
Stolen:
It is subterranean long lateral branch arising from base of the stem. It first grows obliquely upward and then bends down to touch the ground surface. e.g., Colocasia.
 SureDen
SureDen