Golgi apparatus its function and structure
Golgi Apparatus (Baker’s body, Lipochondria)
- Golgi bodies were first detected in nerve cells by Camillo Golgi.
- Found in all cells except RBC of mammals and muscle cells.
- In plant cells the Golgi complex consists of many unconnected units known as dictyosomes.
- Shape is also variable, form a single vesicle (=dictyosomes in plants) to large network like (in neurons) located between the nucleus and the secretory surface. Dictyosomes are present in large number on two side of the equator in dividing plant cells.
Structure:
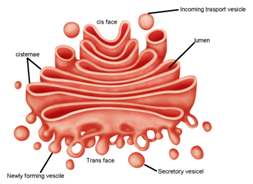
- Three membrane components recognised under the electron microscope are (1) flattened sacs (i.e. cisternae); (2) clusters of tubules and vesicles of about 60 nm; and (3) larger vacuoles filled with an amorphous or granular content.
- The cis or forming face is characterized by the presence of small transition vesicles or tubules that converge upon the Golgi cisternee.
- Associated with the trans or maturing face there is often a saccular structure that is rich in acid phosphatese and has been called the GERL. It has been interpreted as A region of smooth endoplasmic reticulum, near the Golgi, Which is involved in the production of lysosomes.
Origin of Golgi Body from ER:
- Golgi cisternae arise from the RER. The ER releases small vesicles called transition vesicles.
- These vesicles become flat and fuse together to form the forming face (or cis) of the Golgi cisternae.
- The older cisternae come on the maturation (trans) face.
- The forming face points towards the nucleus white the maturing face points towards the exterior of the cell.
Functions of the Golgi Apparatus:
- Glycosidation of lipids and proteins to produce glycolopids and glycoproteins.
- Cell secretion of the enzymes present in lysosomes and peroxisomes.
- Formation of primary lysosomes.
- It synthesizes hemicelluloses and pectic groups of polysaccharides especially during cell division.
- Dictysosomes contain a pool of precursors for the synthesis of certain cell wall materials but they are not involved into the synthesis of cellulose itself.
Related Keywords
 SureDen
SureDen