Oxygen Dissociation curve
Oxygen – Dissociation curve:
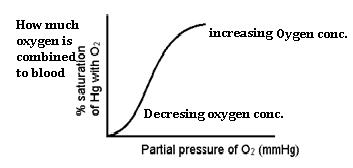
When percentage saturation of hemoglobin with oxygen (O2) , is plotted against the partial pressure of oxygen (Po2), in atmosphere. This plot is called O2-HB Dissociation curve. This Curve is always sigmoid.
Reason for its sigmoid pattern: When Po2 increases, more O2 will binds with HB and blood 97% oxygenated and leaves the lungs but due to more O2 pressure, hemoglobin become less after sometimes and no increase in curve.
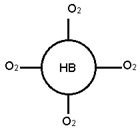
Hemoglobin is red colored Iron pigment in RBCs of blood. One HB molecule can bind with 4 O2 molecules.
Binding of oxygen with hemoglobin to form oxy-hemoglobin depends upon:-
- Partial pressure of O2
- Partial pressure of Co2
- Hydrogen ion concentration
- Temperature:
- In alveoli, there is high Po2, Lesser H+ concentration and low temperature. These factors are favorable for the formation of oxy-hemoglobin.
- In tissues, there is low Po2, high PCo2 , high H+ concentration and high temperature. These conditions are favorable for the dissociation of O2 from oxy-hemoglobin (removal).
- Color of deoxygenated blood: dark purplish red.Color of oxygenated blood: Red.
Effect of PO2 on oxygen Transport:-
As PO2 in blood increases, then more oxygen will bind with hemoglobin (more oxy-hemoglobin will form). It leads to rightward shift of oxygen –HB dissociation curve. Here, hemoglobin become less after a limit. So it starts loosing O2 and passes it to tissues. It is called Bohr’s effect. It plays a crucial role in increasing oxygenation of blood in lungs and release of O2 in tissues.
Haldane effect:- It describes, how oxygen concentration determines heamoglobin affinity towards Co2.
- Like, In high O2 Concentration, O2 binds with heamoglobin and prevent the Co2 to do so.
- And in low O2 Concentration Co2 binds with heamoglobin.
In both cases, O2 is responsible for changes in Co2 concentration in blood. ( Deoxygenation of blood increases its ability to carry Co2 )
Bohr’s effect:- It defines how, Co2 and its ions concentration controls the affinity of HB to bind with O2.
- High Co2 and H+ concentration decreases O2 affinity to bind with HB.
- Low Co2 and H+ concentration increases O2 affinity to bind with HB.
For example:- In working muscles, O2 level is low but Co2 and H+ level is high. So, muscles now get oxygen from oxygenated blood.
 SureDen
SureDen