Distance , Displacement and Speed ,Uniform Speed,Average Speed, Instantaneous Speed
Position
The position of a particle refers to its location in the space at a certain moment of time.
It is concerned with the question - “ where is the particle at a particular instant of time ? ”
Displacement
The change in the position of a moving object is known as displacement. It is the vector joining the initial position of the particle to its final position during an interval of time.
a) Displacement is a vector quantity
b) Dimension : [M0L1T0]
c) Unit : metre (S.I.)
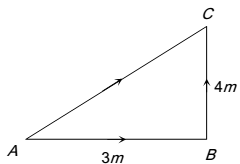
AC=
=5 m
AC is displacement.
Distance
The length of the actual path travelled by a particle during a given time interval is called as distance.
The distance travelled is a scalar quantity which is quite different from displacement. In general, the distance travelled between two points may not be equal to the magnitude of the displacement between the same points.
Dimension : [M0L1T0]
Unit : metre (S.I.)
In the above diagram
AB + BC = 7 m
(3) Comparison between distance and displacement :
(i) The magnitude of displacement is equal to minimum possible distance between two positions.
So distance is greater than or equal to Displacement .
(ii) For a moving particle distance can never be negative or zero while displacement can be.
(zero displacement may mean that body after motion has came back to initial position)
i.e., Distance > 0 but Displacement > = or < 0
(iii) For motion between two points displacement has only one value while distance depends on actual path and so can have many values.
(iv) For a moving particle distance can never decrease with time while displacement can.
(v) Distance can be equal to Displacement if the motion is along a straight line without change in direction.
Speed
Rate of distance covered with time is called speed.
a) It is a scalar Quantity
b)Dimension : [M0L1T–1]
c)S.I Unit : metre/second
d) Speed is always positive or zero i.e it cannot be negative
e) Speed of a moving particle is always greater than zero.
Types of speed :
Uniform speed : When a particle covers equal distances in equal intervals of time, then it is said to be moving with uniform speed.
Non-uniform (variable) speed : In non-uniform speed particle covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time.
Average speed : Average speed is defined as the total path length travelled divided by the total time interval during which the motion has taken place.
a) Average speed =Distance Travelled / Time Taken =
b) Average speed cannot be negative
c) If the motion of a particle is along a straight line and in same direction then, average velocity = average speed.
d) Average speed is, in general, greater than the magnitude of average velocity.
Different Cases for Average Speed
Case 1:When particle moves with different uniform speed v1 ,v2 , v3 ... etc in different time intervals t1, t2, t3 etc respectively, its average speed .
=
Case 2: When particle moves ist moves with uniform speed v1 for time t and then with v2 for same time interval t, its average speed is
Case 3: When a particle describes different distances s1, s2, s3… with different time intervals t1, t2, t3…. with speed v1, v2, v3 …… respectively then the speed of particle averaged over the total distance can be given as
Case4: When particle moves the first half of a distance at a speed of v1 and second half of the distance at speed v2 then
Instantaneous speed : It is the speed of a particle at particular instant. When we say “speed”, it usually means instantaneous speed.
Instantaneous speed
Speedometer of a vehicle tells instantaneous speed.
 SureDen
SureDen