Types of Friction: Static Friction , Limiting Friction and Kinetic Friction : Laws of Motion :Physics
Friction force is of two types.
a) Static b)Limiting Friction(also kind of static friction) c)Kinetic Friction
a) Static friction : The opposing force that comes into play when one body tends to move over the surface of another, but the actual motion has yet not started is called static friction.
It exists between the two surfaces when there is tendency of relative motion but no relative motion along the two contact surface.
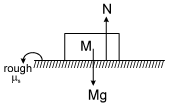
Question : What is value of static friction force on the block?
Answer: In horizontal direction as acceleration is zero. Therefore Σ F = 0 ∴ f = 0
Direction of static friction force :
The static friction force on an object is opposite to its impending motion relative to the surface.
(Importtant!)
Following steps should be followed in determining the direction of static friction force on an object.
(i) Draw the free body diagram with respect to the other object on which it is kept.
(ii) Include pseudo force also if contact surface is accelerating.
(iii) Decide the resultant force and the component parallel to the surface of this resultant force.
(iv) The direction of static friction is opposite to the above component of resultant force.
b) Limiting friction : If the applied force is increased the force of static friction also increases. If the applied force exceeds a certain (maximum) value, the body starts moving. This maximum value of static friction upto which body does not move is called limiting friction.
The magnitude of limiting friction between any two bodies in contact is directly proportional to the normal reaction between them.
Fl ∝ R or Fl = μsR
Direction of the force of limiting friction is always opposite to the direction in which one body is at the verge of moving over the other.
Coefficient of static friction : (a) μs is called coefficient of static friction and defined as the ratio of force of limiting friction and normal reaction
(a) Dimension :
(b) Unit : It has no unit.
(c) Value of μs lies in between 0 and 1
(d) Value of μ depends on material and nature of surfaces in contact that means whether dry or wet ; rough or smooth polished or non-polished.
(e) Value of μ does not depend upon apparent area of contact.
c) Kinetic Friction
Kinetic friction exists between two contact surfaces only when there is relative motion between the two contact surfaces. It stops acting when relative motion between two surfaces ceases. Direction of kinetic friction on an object .It is opposite to the velocity of the object with respect to the other object in contact considered.
Note that its direction is not opposite to the force applied it is opposite to the motion of the body considered which is in contact with the other surface.
Kinetic friction depends upon the normal reaction.
or
where
is called the coefficient of kinetic friction
(ii) Value of μk depends upon the nature of surface in contact.
(iii) Kinetic friction is always lesser than limiting friction ∴
Types of kinetic friction
(a) Sliding friction : The opposing force that comes into play when one body is actually sliding over the surface of the other body is called sliding friction. e.g. A flat block is moving over a horizontal table.
(b) Rolling friction : When objects such as a wheel (disc or ring), sphere or a cylinder rolls over a surface, the force of friction comes into play is called rolling friction.
Rolling friction is directly proportional to the normal reaction (R) and inversely proportional to the radius (r) of the rolling cylinder or wheel.
μr is called coefficient of rolling friction. It would have the dimensions of length and would be measured in metre.
Rolling friction is often quite small as compared to the sliding friction. That is why heavy loads are transported by placing them on carts with wheels.
 SureDen
SureDen