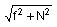Friction and Reasons of Friction:Laws of Motion
Friction
When two bodies are kept in contact, electromagnetic forces act between the charged particles (molecules) at the surfaces of the bodies. Thus, each body exerts a contact force of the other. The magnitudes of the contact forces acting on the two bodies are equal but their directions are opposite and therefore the contact forces obey Newton’s third law.
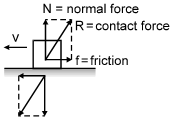
The direction of the contact force acting on a particular body is not necessarily perpendicular to the contact surface. We can resolve this contact force into two components, one perpendicular to the contact surface and the other parallel to it (figure. The perpendicular component is called the normal contact force or normal force ( generally written as N) and the parallel component is called friction.
Therefore if R is contact force then
Reasons for friction
1. Inter-locking of extended parts of one object into the extended parts of the other object.
2. Bonding between the molecules of the two surfaces or objects in contact.
 SureDen
SureDen