Telescope
# Telescope:-
It is an optical instrument used to see the distant objects clearly and magnified
Types of telescopes:- Refracting and reflecting type.
(A) Refracting type telescope:
(I) Astronomical telescope:
Used to see the heavenly bodies (stars, planets etc.)
It produces virtual and inverted image.
(II) Terrestrial telescope:
Used to see the distant objects on earth. It produces an erect image
(I) Astronomical telescope:
Construction:
It consists of two lenses: An objective lens of large focal length and large
Aperture & an eye lens of small focal length and small aperture.
Working:
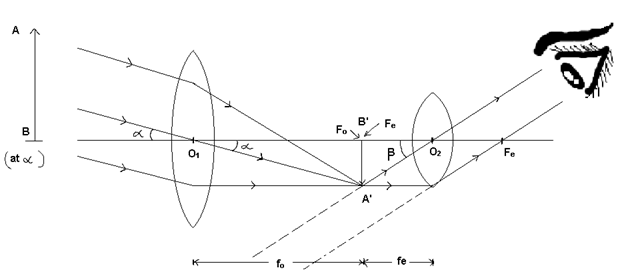
(i) When the final image is formed at ∞ (Normal or Adjustment)
When a 11 beam of light falls on the objective, a real and inverted image A’B’ is formed. If the position of the eye piece is adjusted so that the image A’B’ lies at its focus, then the final highly magnified image is formed at ∞
Magnifying power (M):
M = Angle made by the final image at ∞ the eye/Angle made by the final object At ∞ at the eye seen directly
M = β/∝ = tanβ/tan∝ = A’B’/O2B’/A’B’/O1B’ = O1B’/O2B’ = f0/-fe[∴ M = f0/-fe]
Note: Distance between the two lenses, L = f0 + fe
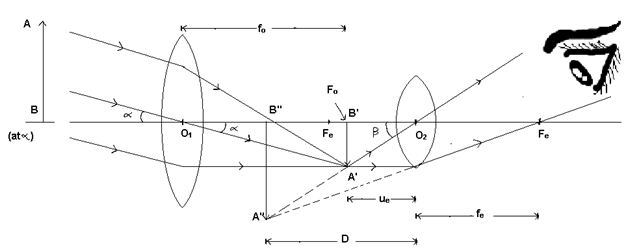
(ii) When the final image is formed at D (Near Point Position)
When a parallel beam of light falls on the object lens, its real and inverted image A’ B’ is formed. The position of the eye piece is adjusted so that the final image A’’ B’’ is formed at D
Magnifying Power(M):-
M = Angle made by the final image (at D) at the eye / Angel made by the object (at ∞)at the eye when seen directly
M = (β/∝) = (tanβ/tan ∝) = (A’B’/O2 B’) / (A’B’/O1B’) = (fo/-ue) ----------- (1)
∴ (1/v) – (1/u) = (1/f)
For eye lens; v = ve = -D, u = -ue, f = +fe
∴ (1/-D) + (1/ue) = (1/fe) ⟹ (1/ue) = (1/fe) + (1/D) = (1/fe)(1 + (fe/D))
Putting in (1), M=(fo/-fe) (1+(fe/D)) length of telescope tube, L = fo + ue
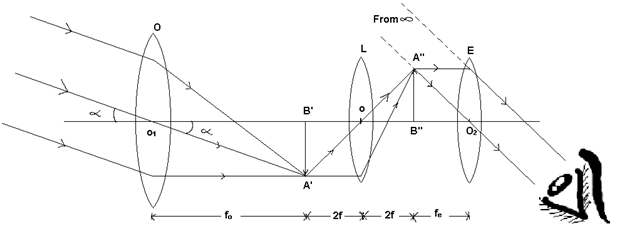
(II) Terrestrial Telescope:
Working
The object lens forms real and inverted image A’B’ of the object. The lens L is held on the principal axis such that B’O = 2f. A real and inverted image A”B” is formed by L. The eyes lens is so adjusted that A”B” lies at its principle focus. The final image formed by the eyes lens is virtual, erect and highly is formed at ∞
- When the final image is formed at ∞: M = fo/-fe
- When the final image is formed at D: M = (fo/-fe)(1+ (fe/D))
(B) Reflecting type telescopes:
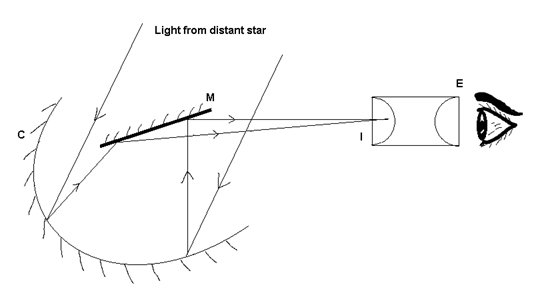
(i) Newtonion reflecting type telescope:
The parallel beam of light coming from the distant star is reflected by a large parabolic concave reflector C on a plane mirror M. The plane mirror reflects the beam forming a real image I in front of an eye piece E.
The eye piece forms a virtual and magnified image of the star magnifying power of telescope M = fo/fe
fo à focal length of concave mirror used as objective, fo = R/2
fe à focal length of eye piece
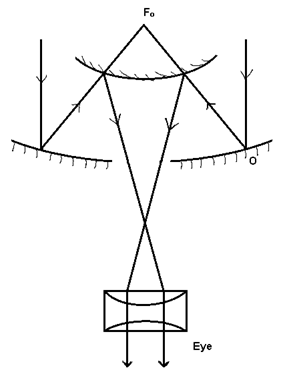
(ii) Cassegrain type telescope:
A parallel beam of light from the distant star falls on objective (o). which converges it towards its principal focus Fo. The reflected beam of light is intercepted by the convex mirror which forms an inverted image seen through eye piece.
Largest telescope of world: Mount Polomer (500 cm. long)and is of cassegrain type:
Advantages of reflecting type telescope over refracting type:
- Spherical aberration is reduced
- These is no chromate aberration.
- Image is brighter
Disadvantages
- They need a lot of adjustments and hence are inconvenient to use.
- They can not be used for general purpose
Difference:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Features of good telescope:
- High magnifying & resolving power
- Large light + gathering power
 SureDen
SureDen