Magnetic Properties
Magnetic Properties:
Substance shows magnetic properties because of presence of electrons in them. Each electron in an atom behaves like a magnet because of its two types of motions - one is around their axis and other around the nucleus. Electrons in an atom because of charge over then and in motion continuously; possess small loop of current which shows the magnetic moment.
Substances are classified into five types on the basis of magnetic properties:
- Paramagnetic
- Diamagnetic
- Ferromagnetic
- Antiferromagnetic
- Ferrimagnetic
(a) Paramagnetism: Substances which are attracted slightly by magnetic field and do not retain the magnetic property after removal of magnetic field are called paramagnetic substances. For example O2, Cu2+, Fe3+, Cr3+, Magnesium, molybdenum, lithium, etc.
Substances show paramagnetism because of presence of unpaired electrons. These unpaired electrons are attracted by magnetic field.
Ex:- O2 (2 unpaired e-) (MOT)
NO, NO2, ClO2 :- all Odd e- Molecules
NO ⟶ N + O
7 + 8 = 15 = 2 x 7 + 1
(b) Diamagnetism: Diamagnetic substances are just opposite to that of paramagnetic. Substances which are repelled slightly by magnetic field are called diamagnetic substances. For example: H2O, NaCl, C6H6, etc. Diamagnetic substances are magnetized slightly when put under magnetic field but in opposite direction.
Substances show diamagnetic property because of presence of paired electrons and no unpaired electron. Thus, pairing of electrons cancels the magnetic property.
Example:- Benzene, C6H6, NaCl, all noble gases, H2O etc.
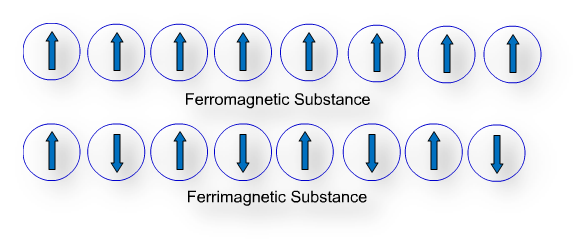
(c) Ferromagnetism: Substances that are attracted strongly with magnetic field are called ferromagnetic substances, such as cobalt, nickel, iron, gadolinium, chromium oxide, etc. Ferromagnetic substances can be permanently magnetized also.
Metal ions of ferromagnetic substances are randomly oriented in normal condition and substances do not act as a magnet. But when metal ions are grouped together in small regions, called domains, each domains act like a tiny magnet and produce strong magnetic field, in such condition ferromagnetic substance act like a magnet. When the ordering of domains in group persists even after removal of magnetic field a ferromagnetic substance becomes a permanent magnet.
Ex:- Fe, Co, Ni, Gd, *CrO2
*Imp. CrO2 ⟶ black colored ferromagnetic oxide of chromium used in manufacturing of audio recording
(d) Anti-ferromagnetism: Substances in which structure are similar to ferromagnetic substances but are oriented oppositely, which cancel the magnetic property are called anti-ferromagnetic substances and this property is called anti-ferromagnetism. They have a net dipole moment zero. For example: MnO .
Ex – Mnfe2O4, fe3O4, MgAl2O4
(e) Ferrimagnetism: Substances which are slightly attracted in magnetic field and in which domains are grouped in parallel and anti-parallel direction but in unequal number, are called ferromagnetic substances and this property is called ferrimagnetism. For example, magnetite (Fe3O4), ferrite (MgFe2O4), ZnFe2O4, etc.
Ferrimagnetic substances lose ferrimagnetism on heating and become paramagnetic.
 SureDen
SureDen