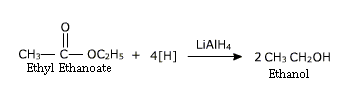Preparation of Monohydric Alcohols
Preparation of monohydric alcohols
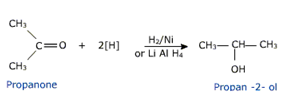
1.From aldehyde and ketones
Aldehydes and ketones are reduced to the corresponding alcohols by
a) Addition of hydrogen in the presence of catalysts like finely divided platinum, palladium, nickel and ruthenium.
This method is called catalytic hydrogenation.
b) Treatment with chemical reagents sodium borohydride (NaBH4) or Lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4).
Aldehydes GIVE primary alcohols while ketones give secondary alcohols.
2. From carboxylic acids and esters
Carboxylic acids are reduced to primary alcohols in the presence of strong reducing agent like lithium aluminium hydride,
Commercially acids are reduced to alcohols by converting them to the esters followed by their reduction using either:
a) Hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst (Catalytic hydrogenation) or
b) Sodium and alcohol.
2. From carboxylic acids and esters
Carboxylic acids are reduced to primary alcohols in the presence of strong reducing agent like lithium aluminium hydride.
From alkenes
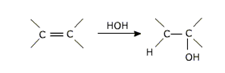
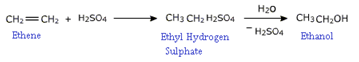
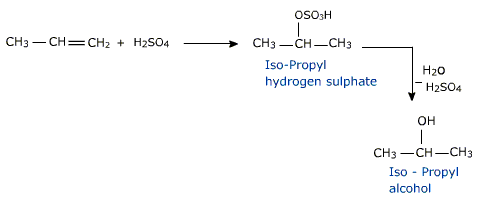
a) Hydration :
Alkenes are absorbed in conc. sulphuric acid forming alkyl hydrogen sulphates.
THE OVERALL PROCESS IS THE ADDITION OF WATER.
The addition of water to the double bond is in accordance with Markownikov's rule. Excepy for the eyhyl alcohol no other primary alcohol can be prepared by this method
The preparation of ethyl alcohol is done starting with ethane.
Similarly isopropyl alcohol is prepared from Propene.
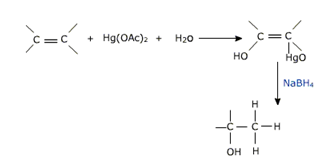
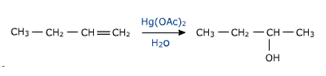
b) Oxymercuration - demercuration
mercuric acetate in presence of water tetrahydrofuran solution reqacts with alkene to form an alkyl mercury compound .
This reaction gives a good yield of alcohol.
The alcohol obtained corresponds to Markownikov's addition of water to the alkene.here the mercury compound is reduced with NaBH4 in basic medium.
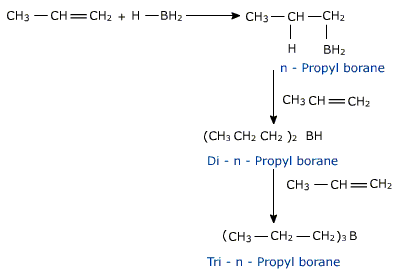
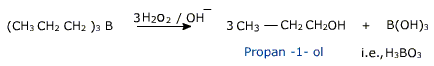
c) Hydroboration
diborane (B2H6), which is an electron deficient molecule(electrophile) to yield alkylboranes (R0B). These are oxidised to alcohols on reaction with hydrogen peroxide in presence of alkali.
In each addition step, the boron atom is attached to the sp2 carbon atom that is bonded to greater number of hydrogen atoms. This overall process occurs with addition of water by anti –markownikoff rule.
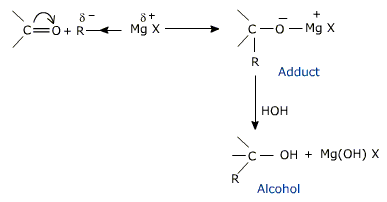
d) From Grignard's reagent
Grignard reagents (R MgX) are alkyl or aryl magnesium halides.
All types of monohydric alcohol can be prepared by use of Grignard reagent,
The C Mg bondin Grignard reagent is a highly polar bond as carbon is electronegative relative to electropositive magnesium.
Grignard reagent form addition compounds by nucleophilic attack with aldehydes and ketone,which on hydrolysis with water or dil.acid yields an alcohol.
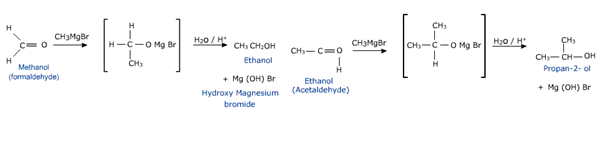
The overall result is to bind the alkyl group of Grignard reagent to carbon of the carbonyl group and hydrogen to oxygen. Formaldehyde gives primary alcohol where as all other aldehydes give secondary alcohols and ketones furnish tertiary alcohols.
 SureDen
SureDen